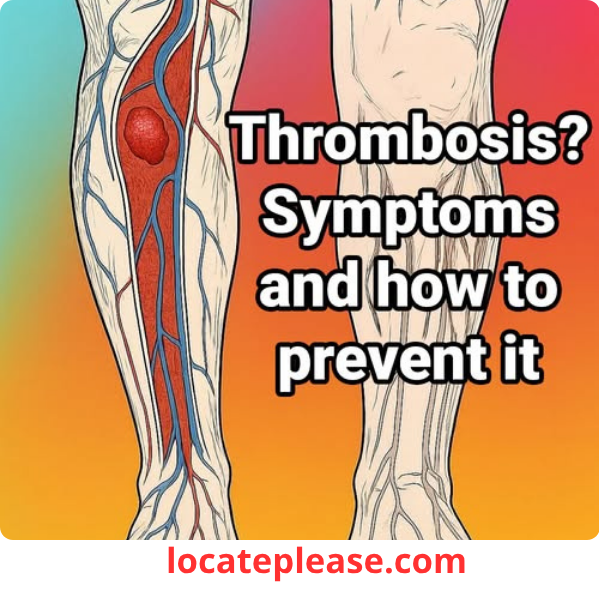
Thrombosis — a blood clot forming inside a blood vessel — is one of the silent killers of our time.
It strikes without warning, often with devastating consequences.
A clot can form in a leg vein and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
It can block a coronary artery, triggering a heart attack.
Or it can obstruct blood flow to the brain, leading to a stroke.
And the scariest part?
You might not feel it coming.
But with awareness, early detection, and smart lifestyle choices, thrombosis is largely preventable.
Let’s break down what thrombosis really is, how to spot the warning signs, and what you can do — naturally — to protect your circulatory system.
What Is Thrombosis?
Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms inside a blood vessel, blocking or restricting blood flow.
There are two main types:
1. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs (sometimes arms)
- Can break loose and travel to the lungs → pulmonary embolism (PE)
2. Arterial Thrombosis
- Clot forms in an artery, often due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis)
- Can cause heart attack or ischemic stroke
Both are medical emergencies — but DVT is often the silent precursor.
Common Symptoms of Thrombosis
Symptoms depend on where the clot forms.
Early detection saves lives.
🚩 In the Legs or Arms (DVT):
- Sudden swelling in one leg or arm
- Pain or tenderness, often starting in the calf
- Warmth in the affected area
- Red or bluish skin discoloration
- Enlarged surface veins (not always visible)
⚠️ Key sign: Swelling and pain in one limb only — not both.
🚩 If the Clot Travels to the Lungs (Pulmonary Embolism):
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Sharp chest pain (worse when breathing in)
- Coughing up blood
- Rapid heartbeat
- Lightheadedness or fainting
👉 This is a 911 emergency.
Do not wait. Act immediately.
🚩 If the Clot Affects the Heart or Brain:
- Chest pain, pressure, or tightness (heart attack)
- Facial drooping, slurred speech, arm weakness (stroke)
Who’s at Higher Risk?
While anyone can develop a blood clot, certain factors increase your risk:
✅ Prolonged immobility
- Long flights or car rides
- Bed rest after surgery or illness
✅ Recent surgery or injury
- Especially hip, knee, or abdominal surgeries
✅ Smoking
- Damages blood vessels and increases clotting factors
✅ Obesity
- Extra weight puts pressure on veins and promotes inflammation
✅ Hormone therapy or birth control pills
- Estrogen can increase clotting risk
✅ Family history of blood clots
- Genetic conditions like Factor V Leiden
✅ Age over 60
- Circulation slows with age
✅ Chronic conditions
- Heart disease, cancer, diabetes, or inflammatory disorders
How to Prevent Thrombosis Naturally
You don’t need medication to reduce your risk — though doctors may prescribe blood thinners in high-risk cases.
For most people, lifestyle changes are your best defense.
1. Stay Active — Move Your Body Daily
- Walking 30 minutes a day boosts circulation
- On long flights or drives, get up and stretch every hour
- Flex your ankles and calves if you must sit
💡 Tip: Calf muscles are called the “second heart” — they pump blood back to your heart.
2. Stay Hydrated
- Dehydration thickens blood, increasing clot risk
- Drink plenty of water, especially when flying or in hot weather
- Limit alcohol and caffeine
3. Eat a Clot-Preventing Diet
Certain foods naturally support healthy blood flow:
✅ Garlic & Onions – Contain compounds that reduce platelet clumping
✅ Turmeric – Curcumin has anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects
✅ Ginger – Natural blood thinner
✅ Leafy greens – Rich in vitamin K (yes, even if on blood thinners — just be consistent)
✅ Fatty fish – Omega-3s reduce inflammation and improve blood fluidity
✅ Berries – Packed with antioxidants that protect blood vessels
Avoid:
❌ Processed foods
❌ Excess sugar
❌ Trans fats
❌ High-sodium meals
4. Wear Compression Socks (If at Risk)
- Especially during travel or if you stand/sit for long periods
- Helps prevent blood pooling in the legs
5. Quit Smoking
- One of the most effective ways to improve vascular health
- Smoking damages vessel walls and increases clotting
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Excess weight increases pressure on leg veins and inflammation
- Even a 10% weight loss can significantly reduce risk
7. Practice Leg Elevation
- At the end of the day, elevate your legs above heart level for 15–20 minutes
- Improves circulation and reduces swelling
Natural Blood Thinners (Use with Caution)
Some natural substances can help reduce clotting — but talk to your doctor if you’re on medication.
- Ginger tea
- Cinnamon
- Cayenne pepper
- Vitamin E (in moderation)
- Willow bark (natural source of salicin, like aspirin)
⚠️ Warning: Don’t combine natural blood thinners with prescription anticoagulants without medical supervision.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any symptoms of DVT or pulmonary embolism, go to the ER immediately.
Even if symptoms seem mild, early treatment can prevent a life-threatening event.
Your doctor may perform:
- Ultrasound (for DVT)
- CT scan or V/Q scan (for lung clots)
- Blood tests (like D-dimer)
Final Thoughts: Prevention Is Power
Thrombosis doesn’t have to be a silent threat.
By knowing the signs, understanding your risk, and adopting simple, natural habits, you can protect your blood vessels and your life.
Your circulatory system is your lifeline.
Treat it with care.
Move. Hydrate. Eat well. Stay alert.
Your blood is flowing — keep it free.